Prevention of Liver Cancer
Prevention of Liver Cancer
High-Risk Groups for Liver Cancer
1.Individuals infected with hepatitis B virus (HBV) and/or hepatitis C virus (HCV).
2.Excessive alcohol drinkers and alcohol abusers.
3.Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) patients.
4.Patients with liver cirrhosis.
5.Individuals with a family history of liver cancer.
6.Men aged 35 and above who have the above conditions.
Prevention of Liver Cancer
1.Vaccination
Vaccination against viruses such as hepatitis A and hepatitis B is recommended. Chronic HBV infection is the most significant cause of liver cancer, with over half of liver cancer patients carrying markers of HBV infection. Hepatitis B vaccination is the most cost-effective and efficient method to prevent HBV infection.
2.Antiviral Treatment
For patients with chronic hepatitis B or C, the goal of treatment is to maximally suppress HBV replication or clear HCV for an extended period. High serum HBV-DNA levels increase the incidence of liver cancer. Smoking and alcohol consumption may further increase the risk of liver cancer in individuals with chronic hepatitis. Therefore, regular antiviral treatment, smoking cessation, and alcohol limitation are recommended to minimize liver damage, prevent the progression to cirrhosis, and ultimately liver cancer.
3.Avoiding Moldy Food
In warm and humid areas, it is essential to ensure the dry and ventilated storage of grain and oil products, minimizing food mold. Do not consume moldy or spoiled food. Avoid the moldiness of bamboo and wooden kitchen utensils, especially cutting boards, chopsticks, and rice scoops. Regular cleaning and proper storage can reduce exposure to aflatoxins. Peanuts, soybeans, rice, flour, vegetable oil, etc., can produce aflatoxins when moldy, and the metabolite aflatoxin B1 has a strong carcinogenic effect on the liver.
4.Balanced Nutrition and Healthy Diet
Maintain a nutritionally balanced, diverse diet with appropriate proportions. Maintain a healthy body weight and blood sugar levels. Avoid pickled and fried foods.
5.Engage in safe behaviors to prevent the transmission of infectious agents.
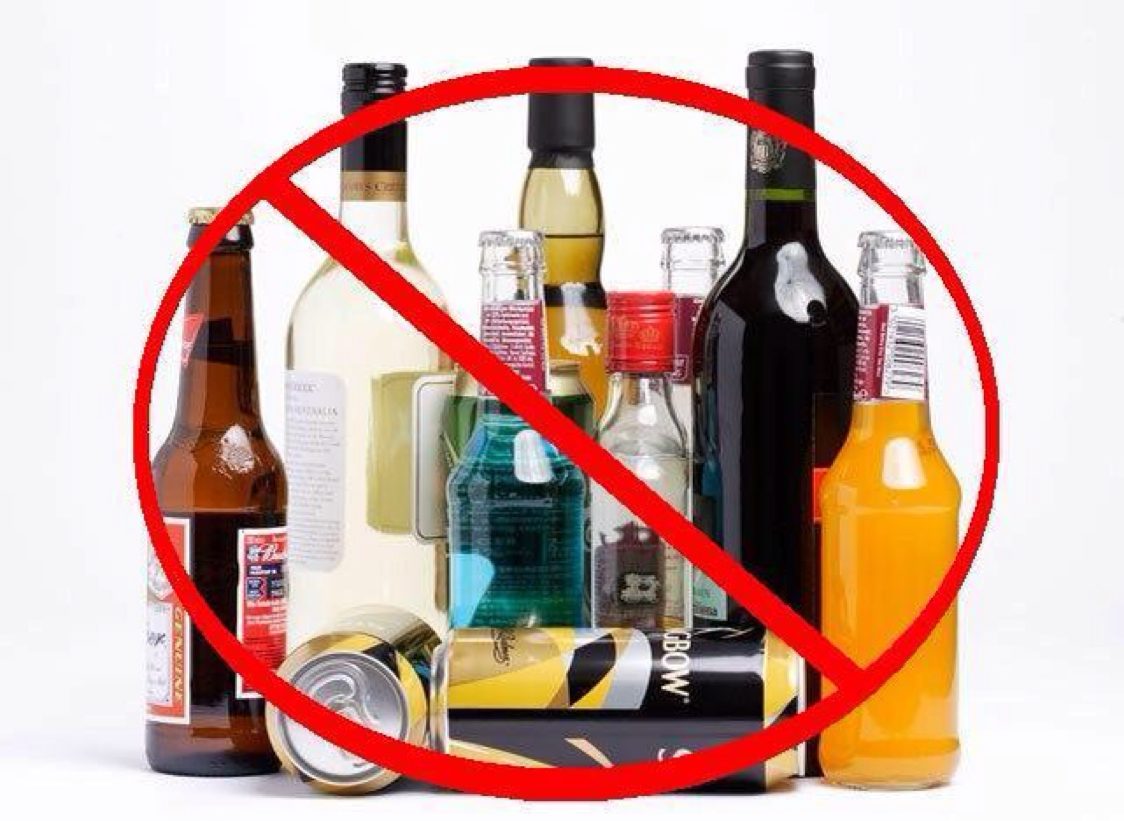

6.Alcohol Abstinence
Abstain from alcohol consumption, as the risk of liver cancer is significantly higher in heavy drinkers. The risk of liver cancer is 2.07 times higher in heavy drinkers compared to non-drinkers.
7.Maintain a Positive Attitude
Avoid excessive emotional fluctuations and strive to maintain emotional stability, avoiding depression and anger.
8.Maintain a Healthy Lifestyle
Follow a regular routine, avoid staying up late, ensure an adequate amount of sleep, and balance work and rest. Staying up late and overexertion can cause various harms to the body, such as endocrine disorders, nervous system imbalances, and a weakened immune system, increasing the risk of liver cancer.
It's important to note that these preventive measures are general recommendations, and individuals should consult with healthcare professionals for personalized advice based on their specific health conditions.




